For materials with high modulus of elasticity young s modulus like zirconia the methods based on resonance frequencies astm e1876 and e1875 are the most practical and accurate choice because.
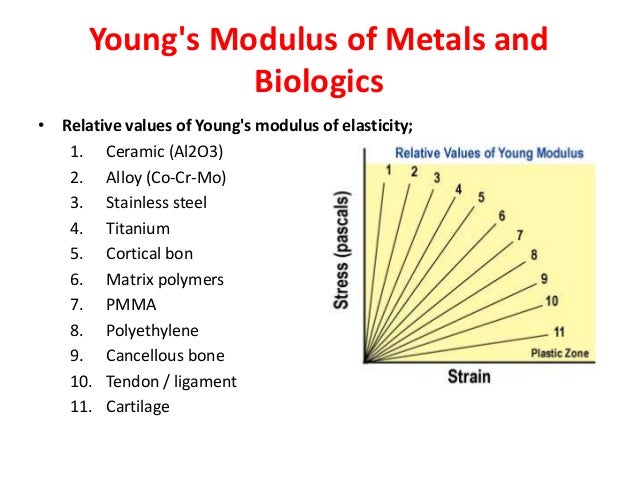
Ceramic young s modulus.
Modulus of elasticity is a measure of stiffness of an elastic material.
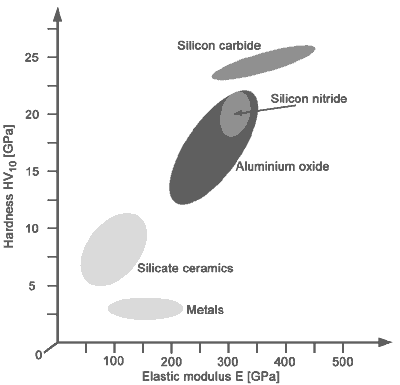
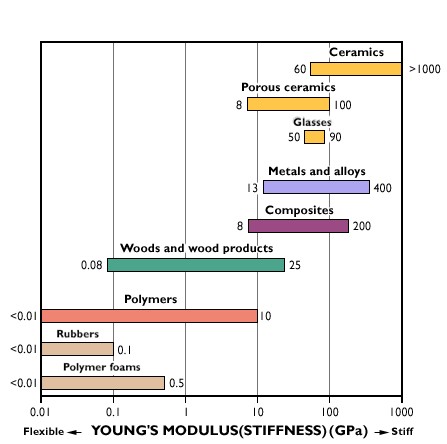
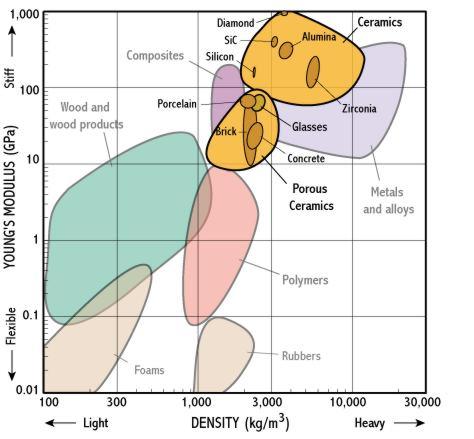
Fine ceramics have high young s modulus ratings.
Mpa x m 1 2.
Young s modulus or tensile modulus alt.
The young s modulus e or the modulus of elasticity of a material determines the level of applied force required before it bends or breaks.
Young s modulus e displaystyle e the young modulus or the modulus of elasticity in tension is a mechanical property that measures the tensile stiffness of a solid material.
Fracture toughness k ic.
Macor young s modulus.
The defects and microstructure of ceramics are crucial to calculate the young s modulus modulus of elasticity poisson s ratio and damping internal friction.
Flexural strength mor mpa r t.
Macor is also a problem solving material combining the performance of a technical ceramic with the versatility of a high performance plastic.
E σ ε displaystyle e frac sigma varepsilon young s moduli are typically so large that they.
Macor has a high use temperature 800 c continuous to 1 000 c peak.
It quantifies the relationship between tensile stress σ displaystyle sigma and axial strain ε displaystyle varepsilon in the linear elastic region of a material and is determined using the formula.
This characteristic determines the force required to cause engineered materials such as silicon nitride ceramics to stretch and deform.
They are rigid and do not easily bend.
Technical datastiffness young s modulus stiffness young s modulus stiffness is measured by young s modulus.
Macor is an outstanding engineering material and is machinable with ordinary metalworking tools.
Poisson s ratio υ.
It describes the constant ratio of tensile stress σ to tensile strain ε within the elastic limits of materials for both tension and compressive forces.
The elastic moduli young s modulus shear modulus and poisson s ratio and damping of polycrystalline materials can be accurately characterized by the non destructive sonelastic systems.
As the number of defects increases the young s modulus modulus of elasticity and poisson s ratio decrease whereas the damping increases.











.jpg)